Git Branch
The git branch command is used to manage branches in a Git repository. Branches are an important feature of Git, as they allow multiple parallel lines of development to take place within a single repository.
- A branch in Git is a separate line of development within a repository. With branches, you can work on multiple independent features or bug fixes within the same repository without affecting the main branch (usually referred to as the “master” branch).
- Once you have finished working on a branch, you can merge it back into the main branch (or into another branch) to combine the changes. Git provides tools for resolving any conflicts that may arise during the merge process.

There are several types of branches in Git, each serving a different purpose:
- Master Branch: The master branch is the default branch in a Git repository. It is the main line of development and is often used to represent the stable version of the code.
- Feature Branches: Feature branches are created to develop new features or improvements in the code. They are separate from the main branch, allowing multiple developers to work on different features simultaneously without affecting each other’s work. When the work on a feature is complete, it can be merged back into the main branch.
- Bugfix Branches: Bugfix branches are created to fix specific bugs in the code. They are separate from the main branch, allowing the developers to focus on fixing the bug without affecting the main line of development. When the bug is fixed, the bugfix branch can be merged back into the main branch.
- Release Branches: Release branches are created to prepare for a new release of the code. They are used to stabilize the code, fix bugs, and test the changes before the release. When the release is ready, the release branch is merged back into the main branch.
- Hotfix Branches: Hotfix branches are created to fix critical bugs in a live or production system. They are branched off from the main branch, allowing the developers to quickly fix the bug without affecting the main line of development. When the hotfix is complete, it is merged back into the main branch and potentially into other branches as well, depending on the branching strategy.
The git branch command is used to manage branches in a Git repository. It allows us to list, create, delete, and switch between branches.
Here are some of the most common uses of the git branch command:
List Branches: To see a list of all the branches in the current repository, use the following command:
$ git branch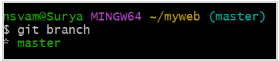
This will display a list of all the branches in the repository, with the current branch indicated by an asterisk (*).
Create a Branch:
To create a new branch, use the following command:
$ git branch <branch-name>
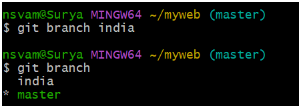
This will create a new branch with the specified name.
Push Branch to remote repo :
To push the created branch to the remote repository, use the following command :
$ git push origin <branch-name> $ git push origin india
Switch to a Branch:
To switch to an existing branch, use the following command:
$ git checkout <branch-name>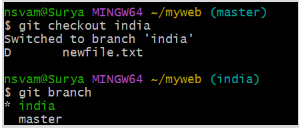
This will switch to the specified branch and update the working tree to reflect its contents.
Delete a Branch:
To delete a branch, use the following command:
$ git branch -d <branch-name>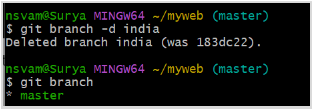
This will delete the specified branch. Note that you cannot delete a branch if it has not been fully merged into another branch.
- To delete a branch in remote repository from the local repository
$ git branch -d <branch-name> $ git push origin -d <branch-name>
These are the basic operations for managing branches in Git. By using branches, you can work on different features or bug fixes in parallel and easily switch between them as needed.
