Git pull/pull request
The git pull command pulls a repository from GitHub. Changes from the remote server are fetched and merged into your working directory.

Developers use pull requests to let other team members know they’ve finished a feature. Whenever their feature branch is ready, they send a pull request to their remote server account. Pull requests tell everyone the code needs to be reviewed and merged into master.
Below is an example of how pull works between different locations and how it differs from other commands.
The “git pull” command
You can pull changes (commits) from a remote repository to your local repository by using the pull command. Local branches get updated with remote-tracking branches. Remote tracking branches are branches that are set up to pull and push from a remote repository. In general, it’s a collection of fetch and merge commands. The first thing it does is fetch the changes from remote and combine them with the local repository.
Here’s how to use pull:
Here’s an example to understand how it works and how to use it. Let’s say I’ve added a new file called ‘pull-file’ to my remote repository of project practice.
In order to create the file, go to the create a file option on the repository sub-functions. Select the file name and edit it as you wish.
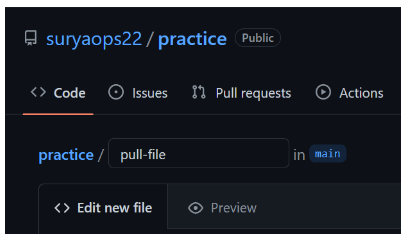
Select a commit message and description for the file. Choose whether you want to create a new branch or commit it directly to the main branch.
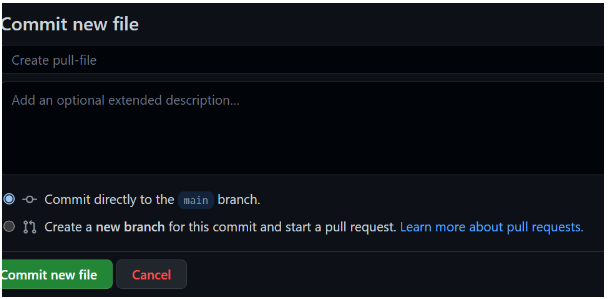
We’ve committed the changes now.
Perform git pull on your cloned repository to pull these changes. There are many options available for pull. Here are a few of them.
Perform Git Pull :
The git pull command is the default way to pull a remote repository. Here’s the syntax:
$ git pullOutput :
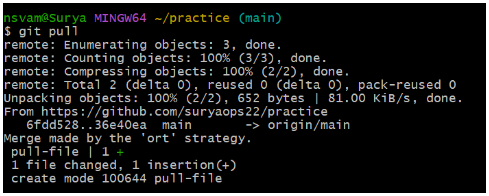
As we can see that the newly created pull-file has been pulled from the remote repo to the local repo.
A git pull command is equivalent to git fetch origin head and git merge head. The head is the current branch.
Git Pull Remote Branch :
We can fetch a branch from Git. Fetching a remote branch is similar to what we did above with the git pull command. The only difference is you have to copy the URL of the branch you want to pull.
Here’s how to pull a remote branch:
$ git pull <remote branch URL>
Output :
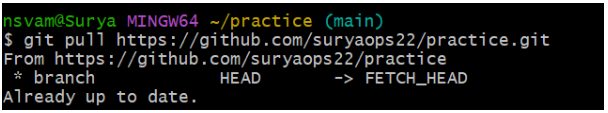
The remote branch edited has been copied in the above output.
Git Pull Origin Master :
The git pull command can also be used to pull the repository. Here’s how it works:
$ git pull origin <branch-name> $ git pull origin main
The term origin refers to the location where the remote repository is located. Main is the main branch.
Here’s what you get:
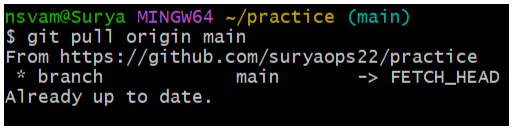
It Data from the local repository will be overwritten by data from the remote repository.
Git pull request :
When you open a pull request, you’re able to discuss and review other people’s changes. It lets you review commits before merging them into the main branch.
You create a pull request when you commit a change in GitHub, and you want other people to review it. You can commit the change to a new branch or an existing branch.
Push commits from your branch once you’ve created a pull request.
How to create a pull request :
Pull requests work because you have to create a file and commit it to a new branch. Earlier in this topic, we talked about committing a file. Click “create a new branch and start a pull request” at the bottom. Name it. Click “propose a new file” at the bottom.
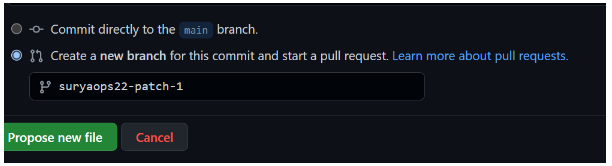
I Select the option to propose a new file. A new page will open. Select the option to create a pull request.
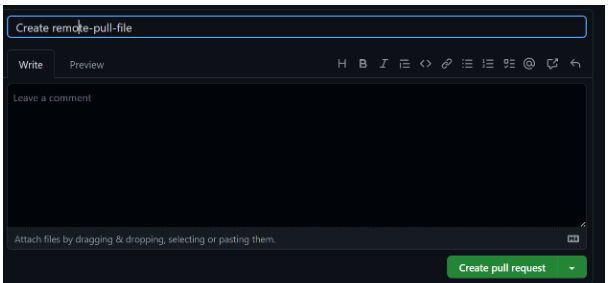
Your pull request is now created. People can see it. They can merge it with other branches by selecting a merged pull request.
