Git Understandings
Version Control system :
A Version Control System (VCS) is a software tool that manages and tracks changes to a project’s source code.
Functions of VCS:
- Allows Developers to work simultaneously.
- Does not allow overwriting each other’s change.
- Maintains a history of every Version.
Types of VCS:
There are two main types of Version Control Systems (VCS):
- Centralized Version Control System (CVCS).
- Distributed/De-Centralized Version Control System (DVCS).
1.Centralized Version Control System :
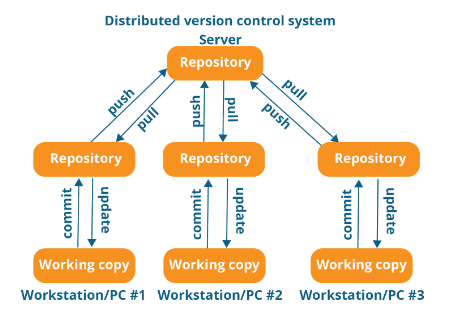
- A CVCS based on Client-Server Architecture, where a central server acts as a single source of truth and stores all the versions of the codebase.
- Client (Developers) access the code from the central server and make changes to it, then the changes are committed to the central repository, which acts as a historical record of all changes made to the code.
Drawback of CVCS:
- Major drawback of CVCS is a single point of failure.
- As all the files are stored in the single source i.e. central server, if the server goes down for an hour, during that one hour no one can collaborate at all.
- Even if Hard-disk corrupts, no one can collaborate because of no backup and entire history will be lost.
- In order to overcome this type of scenario , DVCS came into picture.
2.Distributed/De-Centralized Version Control System :
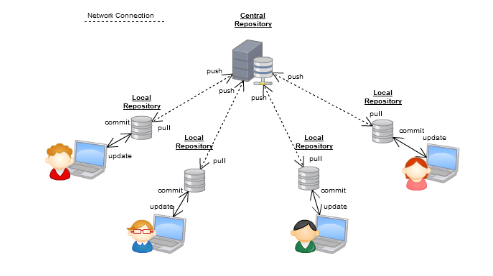
- A DVCS based on peer-to-peer Architecture, where each developer has a complete copy of codebase and its history on their local machine.
- This means each developer acts as both a client and a server and has their local repository that is an exact copy of the central repository.
- In a DVCS, when a developer makes changes to the code, they first make the changes to their local repository. The developer can then push the changes to a central repository or a remote repository hosted on a server. Other developers can then pull the updated code from the remote repository into their local repository.
- In a DVCS, there is no central point of control, which makes it possible for developers to work offline and makes it easier to perform operations like branching and merging.
Ex:- Git & Mercurial
