Power BI – Connect to Excel
To connect to a legacy workbook (such as .xls or .xlsb), the Access Database Engine OLEDB (or ACE) provider is required. Go to the download page and install the appropriate version (32-bit or 64-bit).
The following error message will appear if you don’t have it installed:
- The ‘Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0’ provider is not registered on the local machine.
- The 32-bit (or 64-bit) version of the Access Database Engine OLEDB provider may be required to read this type of file.
- To download the client software, visit the following site: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=285987.
An ACE installation cannot be performed in a cloud service environment. If you are seeing this error in a cloud host (such as Power Query Online), you will need to use a gateway that has ACE installed to connect to legacy Excel files.
Connect to an Excel workbook from Power Query Desktop
Power Query Desktop can be connected by following these steps:
- In the connector selection, choose Excel.
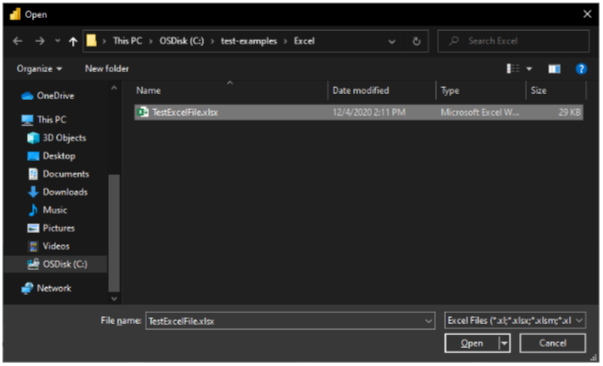
- Select the Excel workbook that you want to load from the file browser. Click on Open.
Using the Web connector, you can connect to an Excel workbook that is online.
3. Select the information you want in Navigator, then either select Load to load the data or Transform Data to continue transforming the data.
Power Query Desktop Navigator imports an Excel workbook.
Connect to an Excel workbook from Power Query Online
To establish the connection through Power Query Online:
- Choose the Excel option from the list of connectors.
- Input the location of the Excel workbook in the Excel dialog box that pops up.
- If required, opt for an on-premises data gateway to access the Excel workbook.
- If this is your initial access to the Excel workbook, choose the authentication method and log in to your account (if necessary).
- In the Navigator, select the desired workbook data and then proceed to transform the data using the Power Query Editor.
Connecting to suggested Tables
When connecting to an Excel workbook that doesn’t have a single table, the Power Query navigator will generate a suggested list of tables that you can select from.
For instance, suppose you have an Excel workbook that includes data from A1 to C5, additional data from D8 to E10, and more data from C13 to F16.
Upon connecting to the data in Power Query, the Power Query navigator produces two lists. The first list encompasses the entire sheet of the workbook, and the second list suggests three tables.
If you choose the entire sheet in the navigator, the workbook will be exhibited in the same form as it appeared in Excel, including null values filling up the blank cells.
If you opt for one of the suggested tables, the navigator will exhibit each distinct table that Power Query could identify from the workbook’s arrangement.
For instance, if you choose Table 3, the data that initially appeared in cells C13 to F16 will be presented.